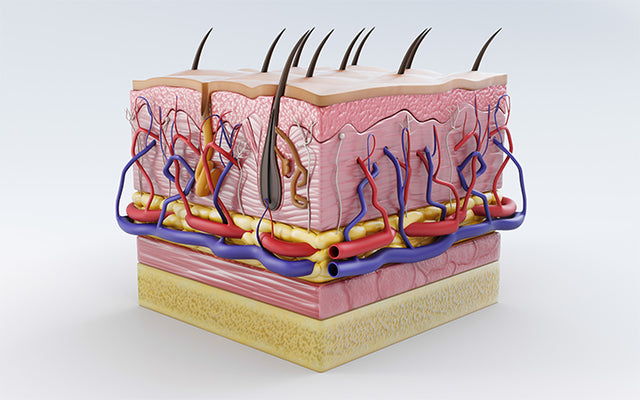
Did you know that your skin performs several vital functions to keep you young and healthy? Various layers in your skin work unanimously to protect you from infections, sun and external damages.
It is also one of the 'gyanendriyas' (sensory organs) that caters to the sensation of 'sparsha' or touch. This is why Ayurveda recommends a good herbal skincare routine that balances your Doshas, keeps the layers of your skin nourished and aids the smooth running of its functions.
Scroll down to know about the different layers of your skin and the myriad functions that each performs.
Highlights:
Histology Of Skin Layers

Your skin is considered to be the largest organ that covers the entire body. It consists of about 7 percent of the total body weight. Composed of 3 unique layers - Epidermis, Dermis and Hypodermis [1], the skin serves a number of important functions.
Skin is the first layer of contact and defense for your body that allows you to perceive your surroundings through the sense of touch and protects you from pathogenic attacks.
The pilosebaceous unit comprising sweat glands, hair follicles, sebaceous gland and arrector pili muscle also forms a part of your skin.
Ayurveda recommends the study of ‘twacha shareer’ or anatomy of the 7 layers of skin for better understanding of your Prakriti (body constitution) and effect of different Doshas on your skin health.
Vitamin E, an important antioxidant that keeps the layers of your skin young and glowing, is supplied to your skin through sebum that is produced by sebaceous glands in the dermis.
How Many Skin Layers Are There In The Human body?

The human skin is formed of three main layers namely, the Epidermis, Dermis and the Hypodermis. The Epidermal layer of skin is further subdivided into five sub-layers - Stratum Basalis, Stratum Spinosum, Stratum Granulosum, Stratum Lucidum, Stratum Corneum [2]. The dermis is also divided into two layers, the Papillary and Reticular Dermis.
The great surgeon of Ayurveda, Sushruta, had cited the presence of 7 layers in the human skin- Avabhasini, Lohita, Shweta, Tamra, Vedini, Rohini and Mansadhara [3]. According to his description of the structure and functions of these skin layers, modern medical science has drawn a parallel with 6 of the skin’s layers as they are recognised today.
|
S.No. |
Skin Layer According To Ayurveda |
Skin Layer According to Modern Medicine |
|
1. |
Avabhasini |
Stratum Corneum Of The Epidermis |
|
2. |
Shweta |
Stratum Lucidum Of The Epidermis |
|
3. |
Tamra |
Stratum Granulosum Of The Epidermis |
|
4. |
Vedini |
Papillary Layer Of The Dermis |
|
5. |
Rohini |
Reticular Layer Of the Dermis |
|
6. |
Mansadhara |
Hypodermis |
“Ayurveda also classifies its skin diseases based on the layers of the skin that it affects,” says Dr. Zeel Gandhi, Chief Ayurvedic Doctor at Vedix.
Structure Of Individual Layers Of Skin

A. Structure Of Epidermis Layer Of Skin
The epidermis is mainly made up of keratinocytes in different stages of differentiation or alteration. In addition to keratinocytes, there are Melanocytes (cells that produce melanin), Langerhans cells (these trigger immune response in case of tissue damage or pathogen attack) and Merkel cells (act as sensory receptors). The epidermis is divided into 5 layers that are explained below.
1. Stratum Basalis
Stratum Basalis is the lowermost layer of the epidermis that is closest to the dermis. Active proliferation of basal cells occur in this layer, some of which travel up and differentiate to form the upper corneocytes. The other types of cells present in this layer of the skin are the melanocytes that produce the pigment melanin, which gives your skin its unique colour and protects you from sun damage.
2. Stratum Spinosum
The cells in the stratum spinosum are glued together by specialized protein complexes known as desmosomes. This gives the stratum spinosum its unique spine-like structure. The squamous layer of the skin can be around 10 layers thick, making it the thickest layer in the epidermis. It also hosts the Langerhans cells that alert your body in case of a pathogen invasion.
3. Stratum Granulosum
This layer of the epidermis derives its name from the presence of granules that contain lipids which moisturize and protect your skin. Being close to the stratum corneum, cells in this layer gradually begin to keratinize.
4. Stratum Lucidum
Only areas which have thick skin have the stratum lucidum. It is made up of dead keratinocytes that provide added protection to areas that are more exposed to external damages such as the palms of your hand and the soles of your feet.
5. Stratum Corneum
The uppermost layer of the epidermis is made of corneocytes. These are keratinocytes that have migrated up from the basal layer and gone through mutation. Due to the mutation, these cells lose their potential to divide and form new cells. The stratum corneum has around 15 layers of flattened skin cells. This hardened layer of corneocytes held in the lipid matrix forms the skin barrier that protects you from external damages.
B. Structure Of Dermis Layer Of Skin

The dermal layer of skin is formed of connective tissues that contain collagen and elastin and provide structure, firmness and elasticity to your skin. The dermis [4] is composed of two parts namely the Papillary Dermis and the Reticular Dermis.
1. Papillary Dermis
The papillary dermis has nerve endings that provide the sensation of touch. It also has blood vessels that bring nutrition to the epidermal layer of your skin.
2. Reticular Dermis
Sweat glands, sebaceous glands and hair follicles are present in this layer of the dermis. The reticular dermis is a thick layer of connective tissues that forms the major part of the dermis.
C. Structure Of Hypodermis Layer Of Skin
The hypodermis is the deepest layer of your skin lying below the dermis. Formed of adipose and connective tissues, this layer stores fat and assists in thermoregulation.
Vedix Tip:
Prepare an Ayurvedic lepa (pack) with turmeric, triphala, yashtimadhu and ashwagandha. Add ghee or honey to this and apply 2 to 3 times a week for healthy, firm skin. Also massaging your skin with oils that have a high content of Vitamin E (coconut, almond) helps in strengthening your skin barrier and reducing oxidative stress.
Functions Of Different Layers Of Skin
From the ‘Kriyatamaka’ or functionary aspect, the different layers of your skin are invested with unique support systems that help it to carry out its various functions.
According to the ancient science of Ayurveda, the three Doshas or bodily humours play an important role in the smooth running of skin functions. An imbalance of the Vata, Pitta and Kapha Doshas can directly interfere with skin functions resulting in the accumulation of harmful Ama toxins in your skin and a vitiation of the Rakta Dhatu (blood tissue). This can lead to various skin issues like dryness, acne, eczema, infection, hyperpigmentation, discolouration and premature skin ageing.
A. Functions Of The Epidermis

1. Skin Barrier
The epidermis acts like a protective barrier against pathogens and mechanical and thermal stress. It also protects the underlying tissues, muscles and organs from external damages. Sebum, sweat and secretions from your natural microbiome (good bacteria that lives on your skin) make up the acid mantle, a protective layer that prevents the growth and invasion of harmful microbes. Moreover, Langerhans cells present in the epidermis immediately signal your immune system in case of infection or injury to the body.
2. Retains Moisture
Moisture retention is an important function of the epidermal layer. The cells in the stratum corneum are bound together in a lipid matrix that prevent water loss from the surface of your skin. This is crucial for maintaining healthy skin. Skin that has a depleted lipid matrix often faces issues such as dryness, eczema, wrinkles and premature skin ageing.
3. Produces Melanin
The epidermis protects your body from the harmful UV rays of the sun that can cause cell damage and skin cancer. Whenever your skin is over exposed to the sun, melanin synthesized in the stratum basalis is transferred to the stratum corneum by melanosomes to deflect and absorb UV radiation (UVA and UVB rays). This is why you happen to tan under the sun.
The pigment melanin also gives you your skin colour. According to Ayurveda, the ‘Bhrajaka Pitta Dosha’ that is seated in the skin helps regulate melanin production. However, an aggravation of the Bhrajaka Pitta can cause overproduction of melanin, resulting in hyperpigmentation. This can lead to skin problems like age spots and melasma.
4. Sensation
Merkel cells present in the basale layer of the epidermis lie close to the nerve endings in the dermal layer. These assist in perceiving the sensations of touch, temperature, pressure and pain.
5. Synthesis Of Vitamin D
Vitamin D is critical for maintaining skin health and running its various functions. From strengthening the epidermal barrier, fostering hair growth to cell renewal, Vitamin D plays a key role. One of the main functions of the epidermis is the synthesis of Vitamin D [5]. Keratinocytes in the epidermis have special enzymes that can convert 7-dehydrocholesterol into Vitamin D when exposed to the sun.
B. Functions Of The Dermis

1. Nourishment
The dermis is a highly vascular skin layer, meaning it has lots of blood vessels that bring nutrition to the upper epidermal layers. Moreover, sebum produced by sebaceous glands present in the dermis nourish and moisturize your skin. This prevents dry skin and premature skin ageing.
2. Thermoregulation
Being part of the integumentary system, the dermal layer of skin plays an important role in regulating body temperature. Optimum body temperature is required for the smooth generation and function of body enzymes. When there is a rise in body temperature, the hypothalamus signals your sweat glands present in the dermis to release sweat.
Through the evaporation of sweat from the epidermal surface, your body releases excess heat. Body heat is also reduced by increasing the subcutaneous blood flow. Blood vessels in the dermis dilate to bring excess blood to the skin. This allows for heat to escape from the surface of your skin.
When there is a drop in temperatures, the blood vessels constrict and sweat production is controlled to trap heat inside your body.
3. Sensation
Sensory receptors present in the dermal layer of your skin allow for perceptions of touch. Due to their presence you can feel the temperature, pressure and texture of the objects that you touch. There are around 3 main types of tactile receptors, each equipped for different sensations or stimuli.
Mechanoreceptors are for sensing mechanical forces such as stretches, pressure, texture, vibrations on the skin. Thermoreceptors sense temperature changes around you. Reflex actions when you touch something hot or cold are controlled by your brain depending on the signals sent by these receptors. Nociceptors sense pain.
4. Excretion And Absorption
Your skin also eliminates body wastes through the sweat produced by sweat glands present in the dermis. Excess water, urea, salts (mainly sodium and chloride) are excreted through sweat to maintain their optimum levels in your blood.
The skin acts as a semi-permeable layer that allows certain fat soluble vitamins to enter and nourish the skin. It also allows for topical drug absorption to fight skin issues and infections.
5. Immunity Against Infections
The dermis hosts a vast number of immune cells such as lymphatic vessels, dendritic cells, killer cells and others. In case of an injury that results in the damage of the epidermal barrier, these immune cells help fight off opportunistic pathogens and prevent chances of infection.
C. Functions Of The Hypodermis
1. Energy Reserve
The hypodermis is the deepest layer of your skin that stores fat which aids in thermoregulation. It also acts as an energy store house for the body.
2. Cushioning
Being a layer of fatty tissues, the hypodermis provides added protection from injuries. It absorbs shocks and pressures and prevents damage to the muscles and organs underneath it. It also provides structure and support to the upper layers of the skin.
How Long Does A Layer Of Skin Last?
The epidermal layer constantly renews itself through the process of cell renewal. Dead cells in the stratum corneum are constantly desquamated. These are replaced by new cells that migrate upward from the basal layers of the epidermis. Complete cell turnover can take around 27 days when the entire upper layer is replaced by new healthy cells.
The Last Word
Different layers of your skin are entrusted with unique functions that nourish, protect and cleanse your body. From keeping pathogenic microbes at bay, synthesizing Vitamin D to acting as a prime sensory organ, the human skin does it all. Sweat produced by your sweat glands helps maintain optimum body temperature and cleans your body of excess salt, water and other wastes.
This is why Ayurveda emphasises on following a good herbal skincare regime, wholesome diet and a stress-free lifestyle that further enhances your skin health. So get your Doshas checked to determine the perfect Ayurvedic skincare and diet that holistically nourishes and fortifies your skin layers from external damaging factors.
Know Your Dosha NowRecommended Products
Was this Article helpful?
- Least helpful
- Most helpful